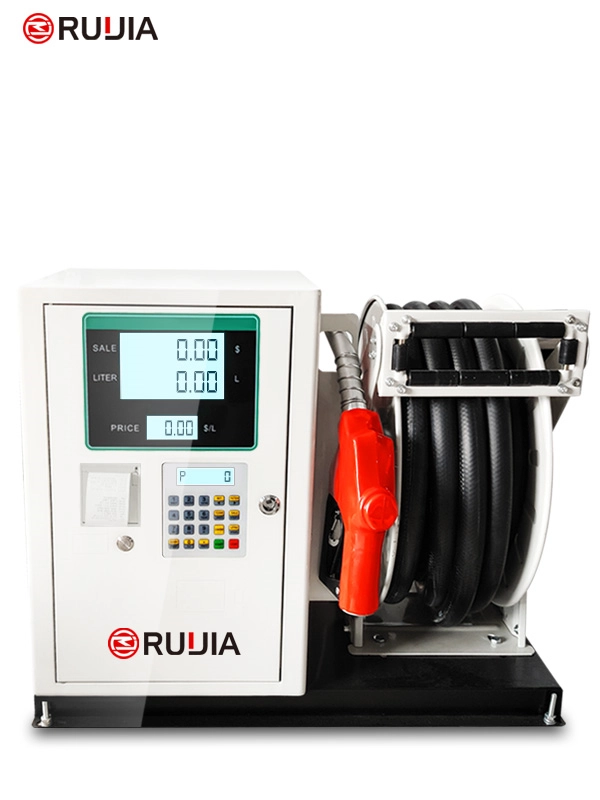
What if the machine that fuels your car vanished overnight? Chaos, right? Gas stations would turn into parking lots. Delivery trucks would idle, stuck. The world, as we know it, would hit pause. That machine—the one you barely glance at while swiping your card—is the fuel dispenser pump. But what is it, really? Not just a metal box with a nozzle. Let’s dig in.
Picture this: You pull up to a gas station, open your car’s fuel door, and grab the nozzle. Squeeze. Fuel flows. Simple? Hardly. That “simple” action triggers a symphony of parts working in unison—parts you’ve never seen, doing jobs you’ve never considered. Ever wonder why the flow stops when the tank’s full? Or how it measures exactly 12.7 gallons? That’s the dispenser’s secret sauce.
Let’s start with the basics, but don’t mistake basics for simplicity. A fuel dispenser pump is the interface between an underground storage tank and your vehicle’s fuel tank. It’s a translator, of sorts—taking fuel from a buried reservoir and delivering it, at the right pressure, in the right amount, to your car. But reduce it to that, and you’re missing the drama. Think of it as a bridge: sturdy, precise, and utterly essential. Without it, the bridge between supply and demand collapses.
Beneath that shiny exterior lies a maze. Let’s peek inside. First, the suction pump—though “suction” is a misnomer. Modern dispensers don’t suck fuel up; they push it. A motor-driven pump, often submerged in the storage tank or mounted nearby, pressurizes the fuel, sending it through a network of hoses. Why pressure? Imagine trying to pour a gallon of milk into a bottle from six feet away—you’d make a mess. Pressure turns chaos into control.
Then there’s the metering device. This is where precision lives. A series of gears or turbines spins as fuel passes through, counting every drop. Ever noticed how the numbers on the display tick up in perfect sync with the flow? That’s the meter, working like a watch’s gears but for liquid. One wrong tooth, and you’d be overcharged—or shortchanged. Manufacturers calibrate these meters to within 0.5% accuracy. Tight, huh?
The nozzle—so simple, yet so clever. That trigger you squeeze? It’s not just a switch. It’s connected to a valve that opens and closes, regulating flow. And that little hole around the nozzle tip? That’s part of the vapor recovery system. Gasoline evaporates quickly; those vapors are harmful and wasteful. The hole sucks them back into the tank, trapping them. Clever, right? Like a vacuum for the air you can’t see.
Ever stopped to think about the hoses? They look rubbery, but they’re anything but ordinary. Reinforced with synthetic fibers, they can withstand pressures up to 50 psi—enough to burst a garden hose. Bend them, yank them, leave them in the sun—they hold. Why? Because a cracked hose isn’t just a spill; it’s a fire hazard. Safety first, always.
What about the display? The one showing price per gallon and total? That’s more than a screen. It’s a computer, communicating with the meter to calculate costs in real time. Some even talk to the gas station’s main system, updating inventory as you pump. Ever wonder how the station knows when to order more fuel? Thank the dispenser’s digital brain.
Not all dispensers are created equal. The one at your local corner store is tiny compared to the giants at truck stops. Those behemoths can pump 50 gallons a minute—enough to fill a semi-truck’s tank in 10 minutes. Try that with a regular nozzle, and you’d be there all day. Then there are marine dispensers, designed for boats. They’re shorter, sturdier, and often have brass components to resist corrosion from saltwater. Different jobs, different tools—makes sense.
Take the Port of Houston, for example. There, marine fuel dispensers—called bunkering units—are monsters. They’re mounted on floating docks, connected to pipelines that snake under the water. These units can pump 2,000 gallons per minute, refueling a cargo ship in hours instead of days. Imagine the pressure: one wrong move, and thousands of gallons could spill into the bay. But they don’t. Why? Because their sensors are military-grade, detecting leaks before they start. A far cry from the nozzle at your neighborhood station, isn’t it?
History buffs, listen up: The first fuel dispensers weren’t pumps at all. In the early 1900s, gasoline was sold in glass bottles, like soda. Then came hand-cranked pumps, bolted to wooden stands, looking more like water wells than modern units. Imagine cranking for five minutes just to get a gallon—how patience must have been a virtue back then! By the 1950s, electric pumps arrived, with the first digital displays in the 1970s. Now? They’re computers on poles, with touchscreens and contactless payment. Progress, huh?
Let’s talk about the unsung heroes: the sensors. Ever had the nozzle click off before the tank’s full? That’s a sensor, detecting when fuel reaches the tip—preventing spills. Some dispensers have sensors that check for leaks in the hoses, shutting down automatically if they find one. Others monitor temperature: fuel expands when hot, so the meter adjusts to give you the correct volume, even on a 90-degree day. Details, details—but details that matter.
In 2019, a gas station in Arizona learned that the hard way. A heatwave pushed temperatures to 115 degrees, and their dispensers’ temperature sensors failed. For three days, customers were charged for more fuel than they received—because hot fuel expands, but the meters didn’t adjust. The state fined the station $12,000. A small price for a big lesson: those tiny sensors aren’t just extras. They’re the law.
Why does this matter? Because the fuel dispenser pump is more than a machine. It’s a piece of infrastructure, as vital as roads or power lines. It’s the reason you can drive to work, to the grocery store, to visit family. It connects the oil refinery to your car, turning crude into motion. Next time you pump, take a second to look—really look. Notice the dents, the faded paint, the way the hose curls. That’s a workhorse, putting in the hours so you can keep moving.
Ever wondered about the colors? Red for gasoline, green for diesel—usually. But not always. In some countries, diesel nozzles are black. In others, premium gas is blue. It’s a global language, but with regional accents. Confusing? Maybe. But then again, the world’s a big place—why should fuel nozzles all speak the same?
What about the future? Could we see dispensers that run on solar power? Maybe. Or ones that talk to your car, automatically syncing with your navigation to suggest the cheapest gas nearby. Some companies are testing dispensers that can fill electric cars’ batteries too—combining fuel and charging in one. Imagine pulling up and choosing: gas or electricity? The dispenser might even know your car’s preference, thanks to Bluetooth. Wild, right?
Shell is already testing such hybrid units in Norway. There, a single dispenser has both a fuel nozzle and a charging port. Electric car owners plug in, while gas car drivers fill up—side by side. The dispenser’s software tracks usage, alerting the station when to restock fuel or boost its electrical grid. It’s a small step, but a glimpse of what’s coming. Who would’ve thought a fuel pump could be eco-friendly?
Let’s get technical—just for a second. The heart of the dispenser is the hydraulic manifold. It’s a block of metal with channels, routing fuel from the pump to the nozzle. Think of it as a traffic controller, directing flow without collisions. Too much pressure, and the fuel sprays; too little, and it trickles. The manifold balances it, like a tightrope walker adjusting their stance with every gust.
And the motor? It’s not just any motor. It’s explosion-proof, sealed tight to prevent sparks—critical when dealing with flammable fuel. Even the switches are designed to avoid sparks. Safety isn’t an afterthought here; it’s built in, from the ground up.
Ever noticed how some dispensers have two nozzles? One for regular, one for premium. How do they switch? Inside, there are two separate lines, each connected to a different storage tank. Flip the switch, and you’re using the premium line. No mixing, no mess. Simple, but effective.
In Alaska, where temperatures drop to -40 degrees, dispensers are built like fortresses. Their motors are wrapped in heaters, their hoses insulated with foam. Why? Because diesel fuel turns into gel in extreme cold. The dispensers there have built-in heaters that warm the fuel as it flows, keeping it liquid. Without them, trucks couldn’t deliver supplies to remote villages. Those dispensers aren’t just machines—they’re lifelines.
Let’s not forget the human touch. Someone has to maintain these machines—checking hoses, calibrating meters, fixing leaks. A good technician can tell if a dispenser is “off” just by the sound it makes. They’re the doctors of the fuel world, keeping the pumps healthy so you can keep driving.
So, what is a fuel dispenser pump? It’s a machine. It’s a tool. It’s a bridge. It’s a story—of innovation, of necessity, of the little things that keep the world turning. Next time you swipe your card and squeeze that nozzle, remember: you’re not just buying fuel. You’re part of a chain that starts in the ground, winds through sensors and hoses and manifolds, and ends with you, moving forward.
Pretty cool, isn’t it?