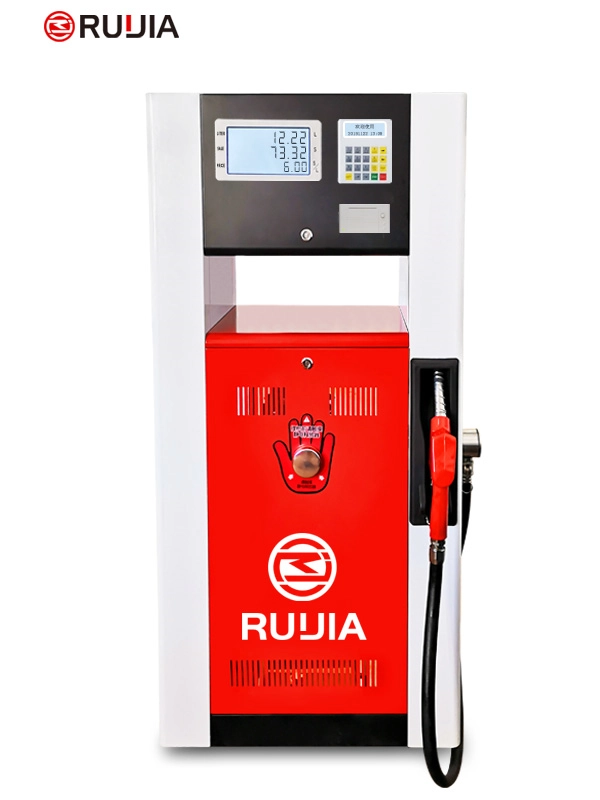
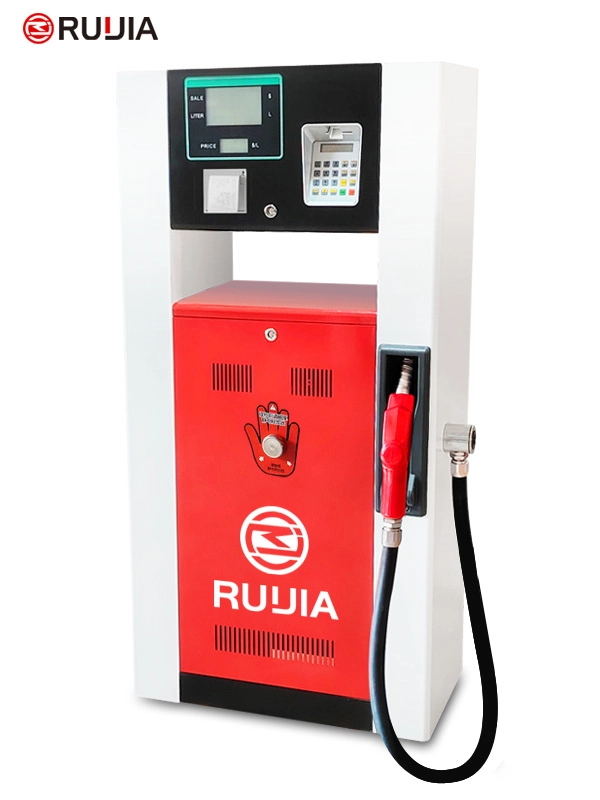
Self-service Petrol Dispenser
Product Parameter
- Product Name
- RJ150X Fuel Dispenser
- Brand Name
- Ruijia
- Product Size
- 800X430X1500mm
- Nozzle
- 1 Nozzles
- Flow Meter
- 4- piston Flow Meter
- Pump
- Vane Pump, Gear Pump
- Lcd Display
- 664, 886
- Temperature
- -25°C~ +55°C
- Pressure
- 0.3MPa
- Accuracy
- ±0.3%
- IC Card
- Supports
- Flow Rate
- 5~60L/min or 5~100L/min
- Voltage
- AC 110V/220V/380V(50/60Hz)
- Suction Distance
- 6m(vertical),50m(horizontal)
- Power
- 750W or 1100W
- Medium
- Gasoline, Diesel, Kerosene
Product Configuration

















Our Certification

What is a Self-Service Petrol Dispenser?
Ever pulled into a petrol station, ready to refuel your car, and found yourself faced with a sleek, imposing machine, sans the familiar attendant waiting to assist? Welcome to the world of self - service petrol dispensers, the modern - day fueling revolution that has transformed the way millions of motorists top up their tanks. But what exactly is this self - sufficient behemoth that has become a fixture at countless fuel stations worldwide? Is it merely a regular petrol dispenser minus the human touch, or does it harbor a wealth of unique features and intricacies? Prepare to embark on a deep - dive exploration into the realm of self - service petrol dispensers, where technology meets convenience in a seamless blend.
At its core, a self - service petrol dispenser is, as the name boldly suggests, a fuel - dispensing apparatus that empowers customers to take matters into their own hands. Gone are the days of idly waiting for an attendant to approach, fuel nozzle in hand. Instead, motorists now step up to the plate, quite literally, assuming the role of their own fueling attendant. It's a shift that might seem simple on the surface, but beneath lies a complex interplay of engineering, technology, and user - centric design. Picture it as a solo performance in a grand theater, where the customer, armed with a fuel nozzle, takes center stage in the refueling process.
The physical structure of a self - service petrol dispenser often mirrors that of its full - service counterpart at first glance. Towering cabinets house the intricate inner workings, with hoses and nozzles extending invitingly, ready to transfer petrol into waiting vehicles. But look closer, and you'll notice subtle yet significant differences. The control panel, for instance, is a focal point of innovation. Unlike traditional dispensers, self - service models feature intuitive interfaces designed to guide customers through the refueling process with ease. Touch - screen displays, often backlit for visibility in all lighting conditions, greet users with a menu of options. From selecting the type of petrol – be it regular unleaded, premium, or diesel in some multi - fuel stations – to authorizing payment, the control panel serves as the command center of the self - service experience. It's like having a personal GPS for refueling, leading customers step - by - step through the process.
Payment systems integrated into self - service petrol dispensers are a marvel of modern technology. In the past, paying for fuel at a self - service station might have involved fumbling for cash or using a clunky card reader. Today, however, the options are vast and convenient. Contactless payment methods, such as tapping a credit or debit card on the reader or using mobile payment apps like Apple Pay or Google Pay, have become the norm. These systems not only speed up the transaction process but also enhance security, reducing the risk of card skimming. Some advanced dispensers even support loyalty card integration, allowing customers to earn points or discounts with every fill - up. It's a seamless blend of finance and fueling, making the payment process as smooth as the petrol flowing into the tank.
Safety, of course, remains a top priority in the design of self - service petrol dispensers. Despite the absence of an attendant, these machines are equipped with an array of safety features that rival, if not surpass, those of full - service models. Automatic shut - off valves in the nozzles are the first line of defense, halting the fuel flow the instant the tank reaches capacity. But self - service dispensers go a step further. Grounding systems, designed to dissipate static electricity, are robustly engineered, as any spark could spell disaster in a petrol - rich environment. Overfill prevention devices, which can detect abnormal fuel levels and trigger an emergency shut - off, add an extra layer of protection. And for those rare moments when things go awry, emergency stop buttons are prominently displayed, easily accessible for customers to halt the fueling process at a moment's notice. It's a fortress of safety, ensuring that customers can refuel with peace of mind.
The inner workings of a self - service petrol dispenser are a symphony of mechanical and electronic components. The pumping mechanism, much like its full - service cousin, is responsible for propelling petrol from the underground storage tanks through the hoses and into the vehicle. High - pressure pumps, driven by powerful electric motors, work tirelessly to ensure a steady flow of fuel. But what sets self - service dispensers apart is their ability to operate independently. Sensors and control systems constantly monitor the fuel flow, pressure, and other vital parameters, adjusting the pump's operation in real - time to maintain optimal performance. It's as if the dispenser has a mind of its own, making split - second decisions to ensure a seamless refueling experience.
Metering systems in self - service petrol dispensers are a testament to precision engineering. Positive displacement meters or turbine flow meters accurately measure the volume of petrol dispensed, ensuring that customers are charged fairly and accurately. These meters are calibrated to the highest standards, with regular checks and adjustments to maintain their accuracy over time. In some advanced models, electronic metering systems use sophisticated algorithms to compensate for factors such as temperature variations, which can affect the density of petrol. This level of precision means that customers can trust that they're getting exactly what they pay for, drop by drop.
The rise of self - service petrol dispensers wasn't a sudden phenomenon. It was a response to a combination of factors, chief among them the growing demand for convenience and cost - efficiency. In a world where time is of the essence, motorists no longer wanted to wait for an attendant to become available. Self - service stations offered a quicker alternative, allowing customers to refuel and be on their way in a matter of minutes. For fuel station operators, self - service models also presented cost - saving opportunities. With fewer attendants required, labor costs were reduced, enabling operators to offer competitive prices to customers. It was a win - win situation that quickly gained traction in the fueling industry.
However, the transition to self - service wasn't without its challenges. Some customers, especially those accustomed to the traditional full - service experience, were initially hesitant. Concerns about operating the machinery, fear of making mistakes, and a general aversion to change were common. To address these concerns, fuel station operators provided clear instructions on the dispensers and in the station premises. Over time, as more and more customers experienced the convenience of self - service, these hesitations faded away. Today, self - service petrol dispensers are not only widely accepted but often preferred by many motorists.
Looking to the future, self - service petrol dispensers are set to undergo even more transformations. The integration of smart technology is already underway, with some stations exploring the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Imagine a dispenser that can recognize your vehicle as you pull up, automatically select your preferred fuel type, and even suggest the best time to refuel based on historical data and real - time price fluctuations. Connectivity is another area of growth, with dispensers potentially being able to communicate with a central system for remote monitoring and maintenance. This would allow operators to detect and address issues before they impact the customer experience, ensuring that the dispensers are always in top - notch condition.
Moreover, as the world shifts towards more sustainable energy sources, self - service petrol dispensers will need to adapt. The rise of electric vehicles and alternative fuels means that these dispensers may need to be retrofitted to accommodate new fuel types or charging options. Some stations are already experimenting with hybrid dispensers that can handle both traditional petrol and electric vehicle charging, a sign of the changing times. It's an exciting era for self - service petrol dispensers, as they continue to evolve and meet the ever - changing needs of motorists and the fueling industry.
In conclusion, self - service petrol dispensers are more than just machines that dispense fuel. They're a symbol of a changing era in the fueling industry, where technology, convenience, and customer empowerment reign supreme. From their intuitive control panels and advanced payment systems to their robust safety features and precision metering, every aspect of these dispensers is designed with the customer in mind. As they continue to evolve and embrace new technologies, self - service petrol dispensers will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in our daily lives, making the refueling experience faster, safer, and more convenient than ever before. So, the next time you pull up to a self - service petrol dispenser, take a moment to appreciate the engineering marvel that's about to fuel your journey. It's not just a machine; it's a gateway to a new era of fueling.
















