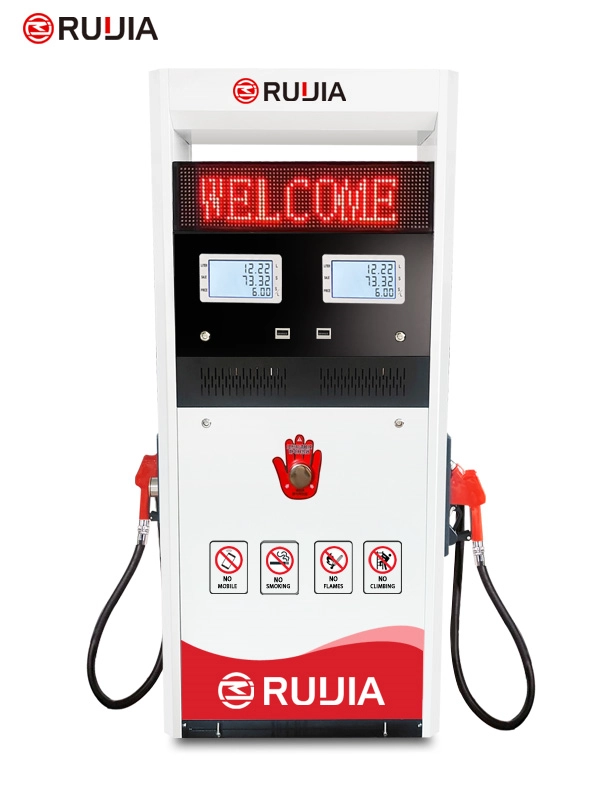
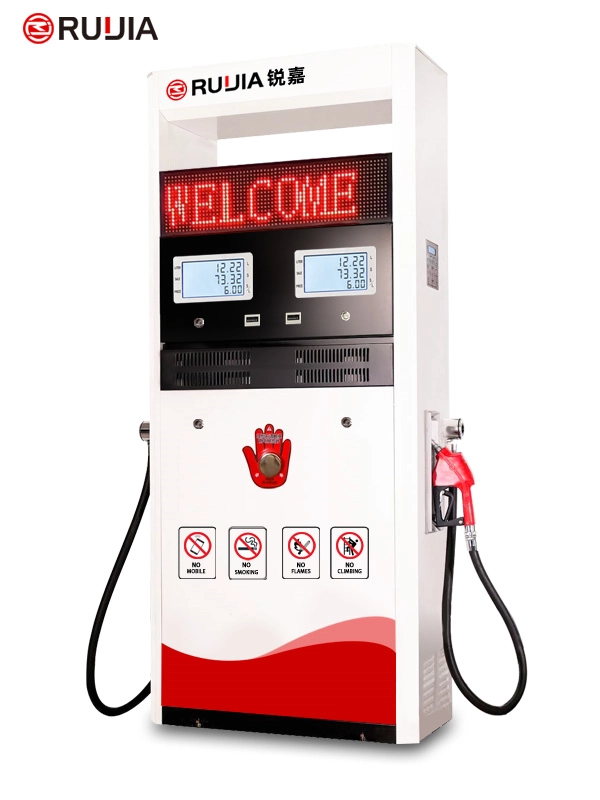
Fuel Dispensing Machine
Product Parameter
- Product Name
- RJ1902 Fuel Dispenser
- Brand Name
- Ruijia
- Product Size
- 1130X570X1900 mm
- Nozzle
- 2 Nozzles
- Flow Meter
- 4- piston Flow Meter
- Pump
- Vane Pump, Gear Pump
- Lcd Display
- 664, 886
- Temperature
- -25°C~ +55°C
- Pressure
- 0.3MPa
- Accuracy
- ±0.3%
- IC Card
- Supports
- Flow Rate
- 5~60L/min or 5~100L/min
- Voltage
- AC 110V/220V/380V(50/60Hz)
- Suction Distance
- 6m(vertical), 50m(horizontal)
- Power
- 750W or 1100W
- Medium
- Gasoline, Diesel, Kerosene
Product Configuration

















Our Certification

What is a Fuel Dispensing Machine?
Ever stood at a gas station, watching the numbers on the fuel dispenser machine's screen tick up as your vehicle guzzles down gasoline, and pondered the enigma behind this everyday contraption? Behold the fuel dispensing machine, a technological sentinel stationed at the crossroads of modern transportation and energy distribution. It's not merely a hunk of metal and wires; it's a sophisticated orchestrator of fuel transfer, a silent yet indispensable workhorse that keeps the wheels of industry, commerce, and personal mobility spinning day in and day out.
At its most fundamental level, a fuel dispensing machine is a specialized apparatus engineered with a singular, crucial mission: to measure, regulate, and deliver fuel from storage reservoirs to vehicles with surgical precision. Imagine it as a meticulous alchemist, carefully concocting and doling out the exact potion of hydrocarbons that your engine needs to roar to life. But peel back the layers of its unassuming exterior, and you'll discover a veritable labyrinth of components, each playing a pivotal role in this intricate dance of fuel delivery.
The metering system, the veritable nerve center of the fuel dispensing machine, reigns supreme in the realm of accuracy. In the industry, two titans of metering technology dominate the landscape: positive displacement meters and turbine flow meters. Positive displacement meters operate on a principle as old as time itself, yet as precise as a Swiss watch. They function by trapping discrete volumes of fuel within their chambers and then methodically transferring them, much like a diligent accountant tallying up coins one by one. Inside these mechanical marvels, pistons or gears move with clockwork precision, ensuring that every drop of fuel is accounted for with astonishing exactness.
Turbine flow meters, on the other hand, are a testament to the elegance of fluid dynamics. As fuel surges through the dispenser's hose, it imparts a whirlwind of force upon a turbine, setting it spinning at a velocity proportional to the flow rate. Sensors, the watchful eyes of the system, detect the turbine's rotational speed and, through a series of complex algorithms, translate that kinetic energy into a precise measurement of the fuel volume dispensed. It's akin to using the revolutions of a windmill's blades to gauge the strength of a gale, but in the high - stakes world of fuel metering. These meters are prized for their ability to handle high - volume flows with lightning - fast response times, making them the go - to choice for busy fueling stations catering to a constant stream of vehicles.
Yet, the metering system is but one cog in the vast machinery of the fuel dispensing machine. Surrounding it is an ecosystem of components, each contributing to the seamless operation of this complex apparatus. The pumping mechanism, a veritable powerhouse, generates the hydraulic might required to propel fuel from the depths of underground storage tanks through the labyrinthine network of hoses and into your vehicle's fuel tank. Electric motors, the workhorses of modern pumping systems, hum away tirelessly, their silent exertions often going unnoticed. But remove these motors from the equation, and the entire fueling process grinds to an abrupt halt, a stark reminder of their indispensable role.
The hoses and nozzles, the tangible interfaces between the machine and the customer, are marvels of engineering in their own right. Crafted from robust materials that can withstand the corrosive nature of fuels and the rigors of daily use, the hoses act as the lifelines through which fuel courses. They're designed with a delicate balance of flexibility and strength, allowing for easy maneuvering around vehicles while maintaining the structural integrity needed to handle high - pressure fuel transfer. The nozzles, meanwhile, are the final gatekeepers of the fueling process. Equipped with state - of - the - art automatic shut - off valves, they're engineered to halt the fuel flow instantaneously when your tank reaches capacity, preventing messy overflows and potential environmental disasters. It's a safety feature so seamlessly integrated into our refueling experience that we often take it for granted, yet it's a crucial safeguard that protects both us and the planet.
And then there's the control panel, the cockpit of the fuel dispensing machine. This is where the magic happens, where customers interact with the machine to select their desired fuel type, authorize payment, and monitor the fueling process. Modern control panels are a far cry from the clunky, mechanical dials of yesteryear. They're sleek, intuitive touch - screen interfaces that often integrate seamlessly with advanced payment systems, loyalty programs, and real - time fuel price displays. It's like having a personal concierge at your fingertips, guiding you through the refueling process with ease and efficiency.
But the functionality of a fuel dispensing machine extends far beyond the simple act of dispensing fuel. In today's highly regulated and technologically advanced world, these machines are veritable fortresses of safety and monitoring. Grounding systems, for instance, are the unsung heroes that safeguard against the ever - present threat of static electricity - induced fires. Static charges can build up during the fueling process, and without a proper grounding mechanism, they could spark a catastrophic inferno. These systems work by providing a conductive pathway for the static charge to dissipate harmlessly into the earth, ensuring the safety of everyone within the vicinity of the fueling station.
Overfill prevention devices add an extra layer of security to the fueling process. While the automatic shut - off valves in the nozzles are designed to stop the fuel flow when the tank is full, these devices act as a failsafe. Using sophisticated sensors, they detect when the fuel level in the tank is approaching its maximum capacity and can trigger an emergency shut - off of the dispenser, even in the event of a malfunction in the nozzle valve. It's a redundant yet essential safety measure that provides peace of mind to both customers and fuel station operators alike.
Modern fuel dispensing machines are also equipped with cutting - edge monitoring capabilities. Data logging systems, the digital memory banks of these machines, record a wealth of information about each fueling transaction. From the time and date of the transaction to the volume of fuel dispensed, the type of fuel, and the price paid, every detail is meticulously logged. This data is a goldmine for fuel station operators, enabling them to track inventory levels, analyze sales trends, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Some advanced systems can even detect anomalies in the fueling process, such as sudden changes in flow rate or abnormal pressure levels, acting as early warning systems that alert operators to potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
The design and construction of fuel dispensing machines are a testament to the ingenuity of engineers. These machines are built to endure the harshest of environments, from the sweltering heat of the desert to the bone - chilling cold of the arctic. The cabinets that house the internal components are constructed from rugged materials such as stainless steel or high - strength polymers, providing protection against corrosion, impact, and the elements. They're also designed with accessibility in mind, allowing technicians to perform maintenance and repairs with ease.
The evolution of fuel dispensing machine technology is a saga of continuous innovation. From the humble beginnings of manual pumps, where customers had to physically operate a lever to draw fuel, to the highly automated, computer - controlled systems of today, the journey has been one of remarkable transformation. The advent of electronic metering systems, for example, revolutionized the industry, replacing old - fashioned mechanical counters with digital sensors and microprocessors. This technological leap not only enhanced measurement accuracy but also paved the way for the integration of advanced features such as remote monitoring and diagnostics.
As the world hurtles towards a more sustainable future, fuel dispensing machines are also evolving to meet the challenges of new fuel technologies. The rise of electric vehicles has spurred the development of charging stations that often coexist with traditional fuel dispensers. Some forward - thinking fuel stations are now equipped with hybrid dispensers that can handle a diverse range of fuels, from conventional gasoline and diesel to alternative energy sources such as hydrogen and biofuels. It's a clear indication that the fuel dispensing machine of tomorrow will be a more versatile and adaptable beast, capable of catering to the ever - changing needs of a rapidly evolving transportation landscape.
In essence, the fuel dispensing machine is a marvel of modern engineering, a complex yet essential piece of infrastructure that we interact with on a daily basis without often giving it a second thought. It's a technological marvel that combines precision, safety, and innovation to ensure that we can refuel our vehicles with ease and confidence. As we look ahead to the future, one thing is certain: the fuel dispensing machine will continue to evolve, adapt, and play a vital role in our energy - dependent world. Whether it's through the adoption of new technologies or the integration of sustainable fuel solutions, this unassuming machine will remain at the forefront of the global fueling industry, silently powering our journey into the future.
















