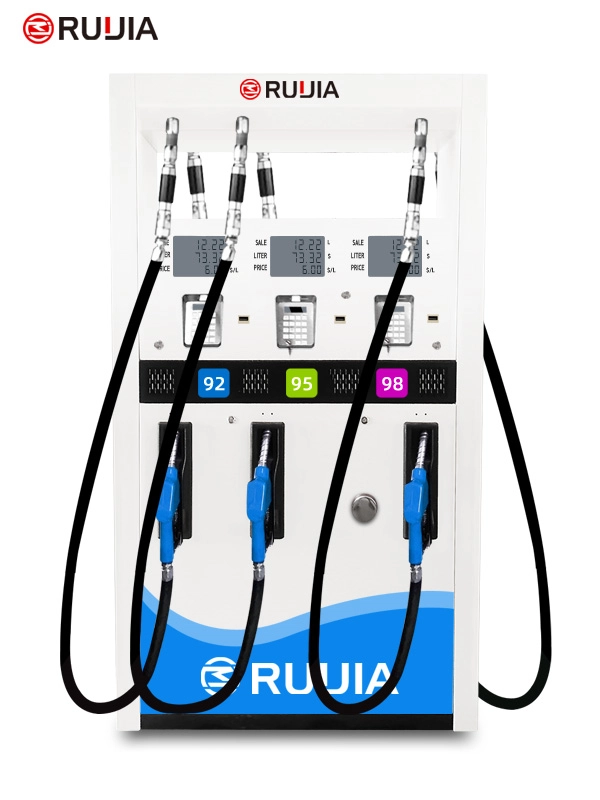
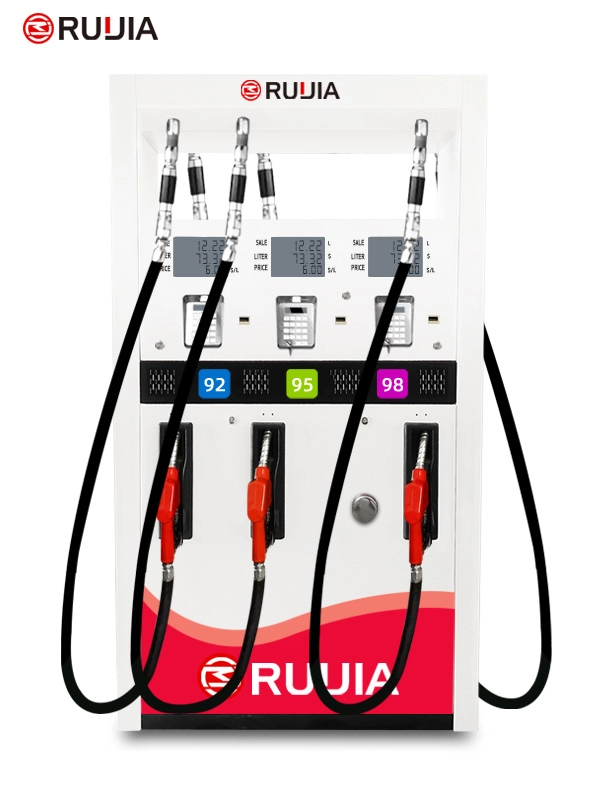
Petrol Dispenser Pump
Product Parameter
- Product Name
- RJ2306 Fuel Dispenser
- Brand Name
- Ruijia
- Product Size
- 1200X560X2250 mm
- Nozzle
- 6 Nozzles
- Flow Meter
- 4- piston Flow Meter
- Pump
- Vane Pump, Gear Pump
- Lcd Display
- 664, 886
- Temperature
- -25°C~ +55°C
- Pressure
- 0.3MPa
- Accuracy
- ±0.3%
- IC Card
- Supports
- Flow Rate
- 5~60L/min or 5~100L/min
- Voltage
- AC 110V/220V/380V(50/60Hz)
- Suction Distance
- 6m(vertical), 50m(horizontal)
- Power
- 750W or 1100W
- Medium
- Gasoline, Diesel, Kerosene
Product Configuration

















Our Certification

What is a Petrol Dispenser Pump?
Ever pulled up to a petrol station, tapped your card, and squeezed the nozzle without a second thought? That machine—glinting in the sun, hose coiled like a lazy snake—does more than just pump fuel. It's a silent conductor, orchestrating a dance of pressure, precision, and safety. But what is a petrol dispenser pump, really? Not just a metal box with a spout. Let's peel back its layers.
Picture this: You select "unleaded," insert the nozzle, and squeeze. Fuel flows. The display ticks upward: £10… £20… £30. Then, a soft click—you let go. Done. Simple? That simplicity is a trick. Inside that casing, parts you've never seen are working overtime: a pump pushing fuel from underground, a meter counting every drop, a sensor ready to halt flow if things go wrong. It's not magic. It's engineering—hidden in plain sight.
Let's start with the core, but don't mistake "core" for "basic." A petrol dispenser pump is the bridge between an underground storage tank and your vehicle's fuel tank. It's a translator, converting raw fuel into a measured, controlled stream. But it's also a guard: it filters out dirt, prevents spills, and stops fires before they spark. Ever wondered why you can't pump petrol into a diesel car by accident? The dispenser's nozzle size is a bouncer—too big for the wrong tank, too small for the right one. Clever, isn't it?
Beneath the hood (so to speak) lies a hydra of components. The heart is often a submersible pump, sitting at the bottom of the underground tank like a diver. It doesn't suck fuel up—it pushes it, with enough force to send it through hoses, past filters, and out the nozzle. Why push instead of suck? Sucking creates vacuums, which can collapse hoses or draw in air. Pushing? Smooth, steady, reliable. That's why modern dispensers favor this method. Old-school "suction pumps" still exist, but they're relics—like using a flip phone in a smartphone world.
Then there's the metering device, the stickler for accuracy. It's a turbine or gear system that spins as fuel passes through. Each rotation equals a tiny volume—say, a tenth of a fluid ounce. The dispenser counts these rotations, translates them into gallons or liters, and—boom—the display updates. But here's the kicker: fuel expands when hot. A liter at 35°C is less fuel than a liter at 15°C. So smart meters adjust for temperature, using sensors to keep counts fair. No cheating—for you or the station.
Safety isn't an afterthought. Static electricity kills around fuel, so dispensers ground themselves with metal cables. Their nozzles? Made of brass, which doesn't spark when rubbed against metal. The hoses? Reinforced with steel mesh, so even if you drive over one (don't try it), it won't burst. And that rubber boot around some nozzles? It's a vapor trapper, sucking back harmful fumes instead of letting them drift into the air. California made these mandatory in the 90s—now they're standard worldwide. Who knew a little rubber could fight smog?
Not all dispensers are created equal. The one at your corner shop is a lightweight compared to highway station giants. A busy motorway dispenser might pump 40 liters a minute—filling a family car in 2 minutes flat. Remote area dispensers? They're rugged, with weatherproof casings to survive rain, snow, or dust storms. Some even run on solar power, no grid needed. In the Australian Outback, a single dispenser might serve a 100-kilometer radius. It's not just a machine there—it's a lifeline.
Let's talk about the oddities. Ever seen a dispenser with two nozzles? One for regular, one for premium. Inside, two separate lines feed them, each connected to its own underground tank. No mixing, no cross-contamination. How do they switch? A valve, triggered by your selection, diverts fuel to the right nozzle. Simple in theory, but misalign that valve, and you could be pumping premium into a regular tank—and charging the customer extra. Ouch.
History buffs, lean in. The first petrol dispensers weren't pumps at all. In 1905, they were glass jars, sold over hardware store counters. By the 1920s, hand-cranked pumps arrived—clunky, slow, prone to spills. Imagine cranking for 5 minutes to get 5 liters! The 1950s brought electric pumps, and the 1970s added digital displays. Now? They're computers on poles: touchscreens, contactless payment, even cameras to spot drive-offs. From jars to AI—what a leap.
Ever noticed the "automatic shutoff"? That's the hero you never thank. A tiny hole near the nozzle tip sucks in air as fuel flows. When your tank fills, fuel blocks the hole, creating a vacuum. The vacuum yanks a lever, slamming the valve shut. No spills, no mess. Invented in 1964, this little feature turned petrol stations from chaos zones into orderly spots. Before that? Attendants had to hover, watching for overflows. Now? You can scroll through your phone while it works. Progress.
What about the numbers on the display? They're not just random. The dispenser's brain—yes, it has one—talks to the meter, updating the total with each spin. It also chats with the station's main system, tracking inventory. Sell 500 liters of unleaded? The system flags it: "Time to restock." Some even send alerts to delivery trucks, so they arrive before the tank runs dry. No more "Sorry, we're out of regular."
Let's get technical—briefly. The "hydraulic manifold" is the traffic cop. It's a block of metal with channels that route fuel from pump to nozzle, bypassing filters if needed (during maintenance, for example). It's also where pressure is regulated. Too much pressure, and fuel sprays; too little, and it dribbles. The manifold balances it, like a bartender pouring a perfect drink—neither too fast nor too slow.
Marine petrol dispensers? They're rebels. Saltwater corrodes metal, so their parts are brass or stainless steel. Their hoses are short and stiff, to reach boat fuel ports without kinking. And they measure fuel by weight, not volume—because waves slosh, and sloshing throws off volume counts. Boats don't play by car rules. Why should their dispensers?
What's next? Dispensers that talk to your car, maybe. Imagine pulling up, and the dispenser reads your tank size via Bluetooth, stopping automatically at 45 liters. Some stations in Europe are testing this—no more guessing, no overfilling. Others are adding EV chargers alongside petrol nozzles: "Fill up on gas or electrons—your call." The future isn't ditching dispensers. It's making them multitask.
Let's end with a story. A petrol station in rural India, 2010. A monsoon floods the underground tanks, but the dispenser's float switch detects water, shutting down. No contaminated fuel sold. A farmer, relying on that station to refuel his tractor, avoids a breakdown during harvest. That switch? A $10 part. The harvest? Priceless. That's the dispenser's quiet job: saving days, dollars, and sometimes livelihoods.
So, what is a petrol dispenser pump? It's a bridge. A guard. A mathematician. A time-saver. It's the reason you can fill up and go, without thinking about the engineering that makes it possible. Next time you squeeze that nozzle, take a second. Look at the dents, the faded logo, the way the hose curls. That's a workhorse—one that keeps the world moving, one liter at a time.
Pretty remarkable, isn't it?
















