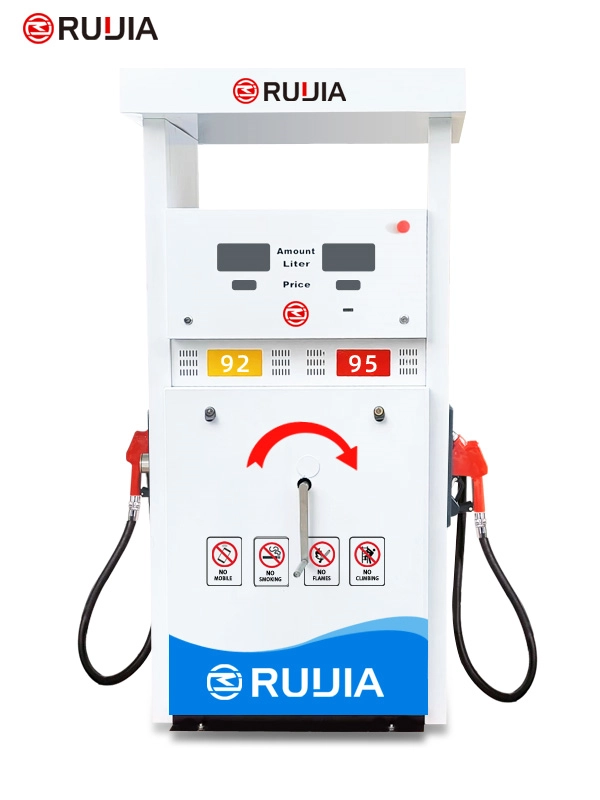
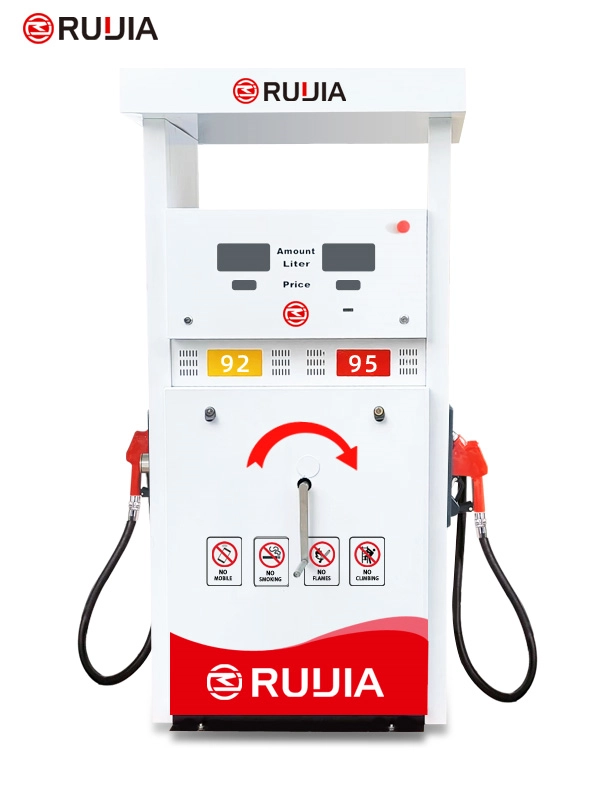
Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump
Product Parameter
- Product Name
- RJSYB Fuel Dispenser
- Brand Name
- Ruijia
- Product Size
- 1130X570X2200 mm
- Nozzle
- 2 Nozzles
- Flow Meter
- 4- piston Flow Meter
- Pump
- Vane Pump, Gear Pump
- Lcd Display
- 664, 886
- Temperature
- -25°C~ +55°C
- Pressure
- 0.3MPa
- Accuracy
- ±0.3%
- Unit Price
- 0.00 to 9999
- Flow Rate
- 5~60L/min or 5~100L/min
- Voltage
- AC 110V/220V/380V(50/60Hz)
- Suction Distance
- 6m(vertical), 50m(horizontal)
- Power
- 750W or 1100W
- Medium
- Gasoline, Diesel, Kerosene
Product Configuration

















Our Certification

What is a Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump?
In the vast landscape of fuel dispensing technology, where automated systems and high-tech gadgets seem to dominate the scene, there exists a humble yet indispensable device - the Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump. At first glance, it might appear as a relic from a bygone era, a mechanical anachronism in our digitized world. But make no mistake; this unassuming apparatus holds a crucial place in numerous industries and settings, defying the odds and continuing to prove its worth time and time again.
Picture this: A remote construction site nestled deep in the mountains, far removed from the reach of electricity and modern fueling infrastructure. Heavy machinery stands idle, waiting for a lifeblood of energy to resume its operations. Enter the Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump. With a simple yet ingenious design, this pump becomes the savior of the site, allowing workers to transfer fuel from storage drums to the machinery with ease. It's a scene that plays out in countless off-grid locations around the world, highlighting the pump's resilience and practicality.
So, what exactly is a Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump? At its core, it's a mechanical device that relies on human power to draw fuel from a storage container and dispense it into a vehicle, equipment, or another receptacle. Unlike its automated counterparts that rely on electricity or complex electronic systems, the manual hand pump operates on the principle of mechanical leverage and suction. A user engages with the pump by operating a handle, which in turn activates a series of internal components to create a vacuum, drawing the fuel up through a hose and out through a nozzle.
The anatomy of a Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump is a marvel of engineering simplicity. Typically, it consists of a durable housing, often made of robust materials like cast iron or high-strength plastic, designed to withstand the rigors of handling flammable liquids. Inside the housing, you'll find a piston or diaphragm mechanism that does the heavy lifting. As the handle is pumped, the piston moves back and forth, creating pressure differentials that propel the fuel forward. Attached to the pump is a flexible hose, usually made of fuel-resistant rubber, which extends to the point of dispensing. The hose is terminated with a nozzle, which not only controls the flow of fuel but also ensures a secure connection to the receiving container.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump is its versatility. It can handle a wide range of fuels, from gasoline and diesel to kerosene and other petroleum-based products. This makes it an invaluable tool in industries such as agriculture, where tractors and other farm equipment need to be fueled in remote fields. Consider a small family farm in the Midwest. The farmer may not have access to a large, automated fuel station on the property. Instead, they rely on a manual hand pump to transfer fuel from a storage tank to their tractors, combines, and other machinery. This not only saves them time and money but also ensures that their operations can continue without interruption, even during power outages or when fuel delivery services are delayed.
In the marine industry, Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pumps are equally essential. Boats and ships, especially smaller vessels and those operating in remote areas, often rely on these pumps to transfer fuel from storage drums or tanks to their engines. Imagine a fishing boat out at sea, miles away from the nearest port. If the boat runs low on fuel, the crew can use a manual hand pump to draw fuel from reserve containers and keep the engines running. It's a matter of survival in some cases, highlighting the critical role that these pumps play in ensuring the safety and functionality of marine vessels.
But the applications of Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pumps don't stop there. They're also commonly used in emergency response situations. During natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, when power grids are down and infrastructure is damaged, these pumps can be a lifeline. Rescue teams can use them to fuel their vehicles, generators, and other equipment, enabling them to reach affected areas and provide much-needed assistance. In a scenario where every minute counts, the simplicity and reliability of a manual hand pump can make all the difference.
Of course, like any mechanical device, the Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump has its limitations. One of the primary drawbacks is the physical effort required to operate it. Pumping fuel by hand can be tiring, especially when large volumes of fuel need to be transferred. This makes it less suitable for high-volume fueling operations in commercial settings where speed and efficiency are paramount. Additionally, manual hand pumps are not as accurate as automated fuel dispensers when it comes to measuring the exact amount of fuel dispensed. While some models come with basic measurement markings on the hose or container, they may not provide the same level of precision as electronic meters.
However, manufacturers are constantly innovating to address these limitations. Some modern Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pumps feature ergonomic designs that reduce the physical strain on the operator. These pumps may have larger, more comfortable handles or improved leverage mechanisms that make pumping easier and more efficient. Others are equipped with advanced flow control features, allowing users to regulate the speed at which fuel is dispensed more accurately.
Looking to the future, the Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump is likely to continue evolving. As the demand for sustainable and off-grid energy solutions grows, there's a potential for these pumps to be integrated with alternative fuel sources. For example, researchers are exploring the use of biofuels and hydrogen in manual fueling systems. While these developments are still in the early stages, they offer a glimpse into the pump's potential for adaptation and survival in an ever-changing technological landscape.
In conclusion, the Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump may not be the most glamorous or high-tech piece of equipment in the world, but its significance cannot be overstated. It's a testament to the power of simple, reliable engineering and its ability to meet the needs of diverse industries and situations. Whether it's keeping a remote construction site operational, fueling a boat in the middle of the ocean, or providing essential support during a natural disaster, this unassuming pump continues to prove its worth day after day. It's a reminder that sometimes, the most valuable tools are the ones that combine functionality with simplicity, and the Manual Fuel Dispenser Hand Pump fits that description to a tee.
















